


Next: Weighting the solution by
Up: Estimation with unknown exposure
Previous: Estimation with unknown exposure
The general case: multiple images with unknown K
It can be seen, from (12)
that changing the value of 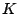 changes only the amplitude
(range scaling) of
changes only the amplitude
(range scaling) of 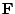 . Therefore,
. Therefore, 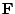 may first be solved using a ``generic'' value of
may first be solved using a ``generic'' value of 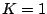 ,
so that the shape of
,
so that the shape of 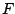 can be found up to another single
unknown scalar constant.
Subsequently, when working with more than two images,
a function
can be found up to another single
unknown scalar constant.
Subsequently, when working with more than two images,
a function 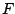 may be found for each image pair, and since all
the estimates of
may be found for each image pair, and since all
the estimates of 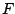 should vary only in overall amplitude,
the curves may be scaled to the same height and averaged to obtain
an average estimate of the general shape of
should vary only in overall amplitude,
the curves may be scaled to the same height and averaged to obtain
an average estimate of the general shape of 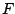 for the entire image
sequence. Then the individual
for the entire image
sequence. Then the individual 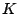 values may be found by comparing
each
values may be found by comparing
each 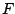 to the averaged
to the averaged 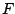 .
.
After a crude solution found by averaging,
as a first of a succession of guesses,
the result may be refined by a least squares fit across all possible pairs
of images.
Alternatively, a combination of averaging and least squares across all pairs
may be made, especially if some pairs turned out to be related by the same
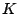 values (in which case comparagrams with like
values (in which case comparagrams with like 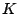 values may be averaged,
to reduce the number of all possible image pairs).
values may be averaged,
to reduce the number of all possible image pairs).
Since 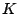 can only be determined up to an unknown offset and gain constant,
without loss of generality, the
can only be determined up to an unknown offset and gain constant,
without loss of generality, the 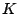 values are assumed to be on the
interval from 0 to 1.
values are assumed to be on the
interval from 0 to 1.
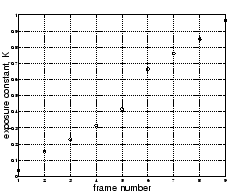
As an example, nine of the eleven test images were used (two were left out),
and the 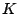 values returned after one iteration appear in Fig 6.
values returned after one iteration appear in Fig 6.
Figure 6:
Estimated exposure values, 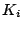 from nine of the eleven test images.
We can clearly see, in the estimated values, where two of the
images were left out of the sequence.
from nine of the eleven test images.
We can clearly see, in the estimated values, where two of the
images were left out of the sequence.
 |



Next: Weighting the solution by
Up: Estimation with unknown exposure
Previous: Estimation with unknown exposure
Steve Mann
2002-05-25
![]() values (in which case comparagrams with like
values (in which case comparagrams with like ![]() values may be averaged,
to reduce the number of all possible image pairs).
values may be averaged,
to reduce the number of all possible image pairs).
![]() can only be determined up to an unknown offset and gain constant,
without loss of generality, the
can only be determined up to an unknown offset and gain constant,
without loss of generality, the ![]() values are assumed to be on the
interval from 0 to 1.
values are assumed to be on the
interval from 0 to 1.
![]() values returned after one iteration appear in Fig 6.
values returned after one iteration appear in Fig 6.
